| Welding is a vital process used across various industries to join metals and create strong, durable structures. There are numerous types of welding methods available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will delve into the different types of welding methods, highlighting their benefits and popular applications. Whether you're a welding professional or someone interested in the field, this comprehensive guide will help you navigate the world of welding methods.
|
|
|
1. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
|
|
|
|
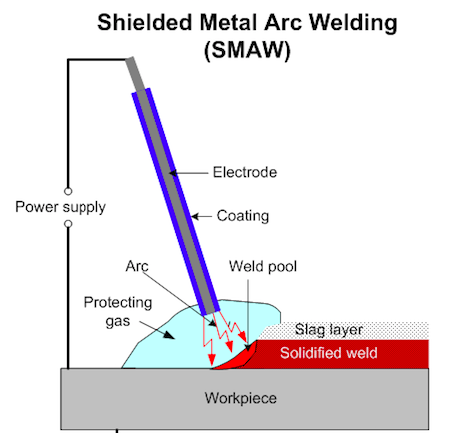
| Shielded Metal Arc Welding, also known as stick welding, is a widely used method that employs a consumable electrode coated in flux. The flux coating acts as a shielding gas, protecting the weld from atmospheric contamination. SMAW is versatile and suitable for various metals, making it commonly used in construction, pipelines, maintenance, and repair work.
|
|
|
|
2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG)
|
|
|
|
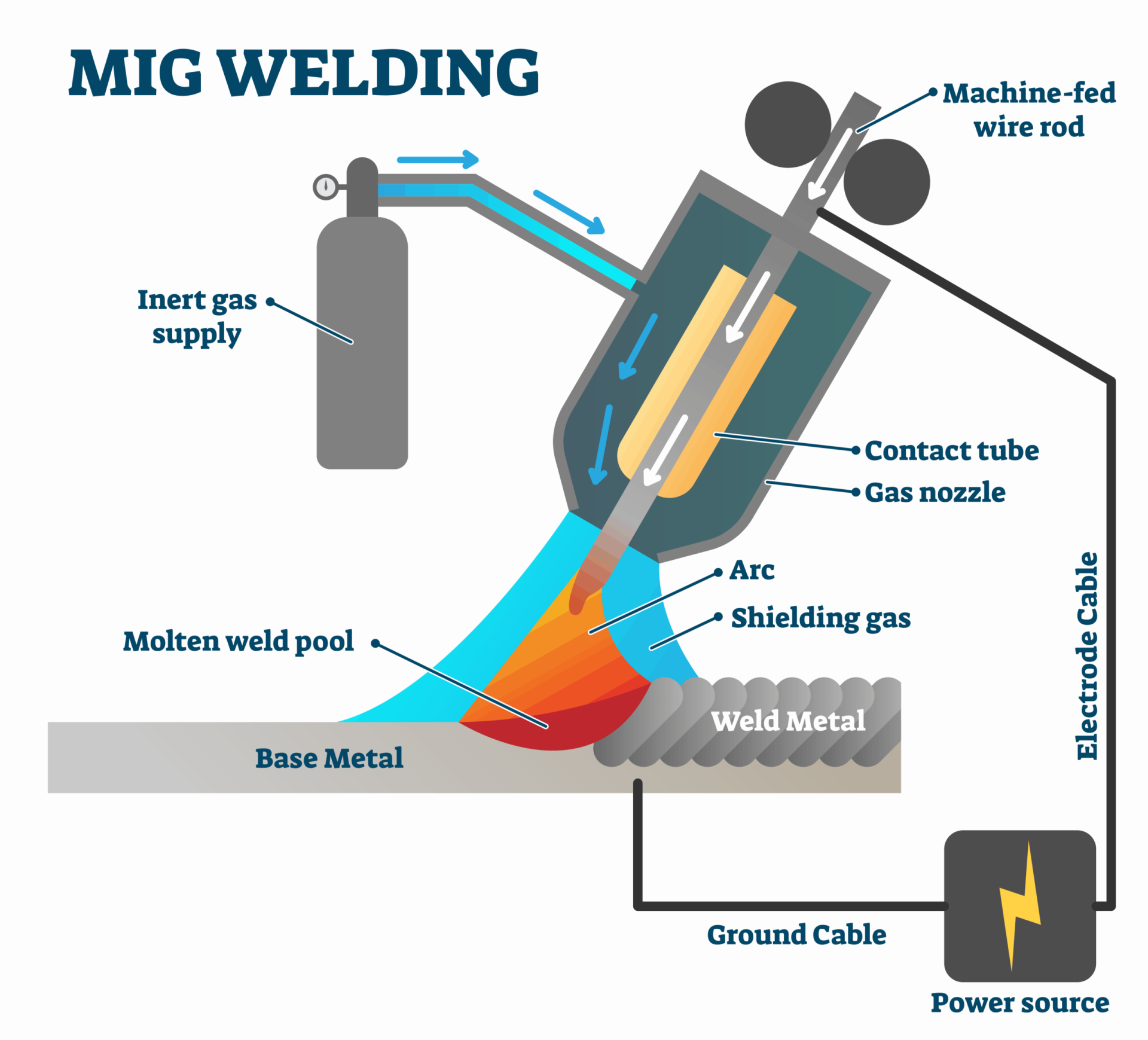
| Gas Metal Arc Welding, also referred to as Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding, utilizes a continuous wire electrode and a shielding gas, typically a mix of argon and carbon dioxide. GMAW is known for its efficiency and speed, making it ideal for high-production manufacturing processes. It is commonly used in automotive, fabrication, and construction industries.
|
|
|
|
3. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
|
|
|
|
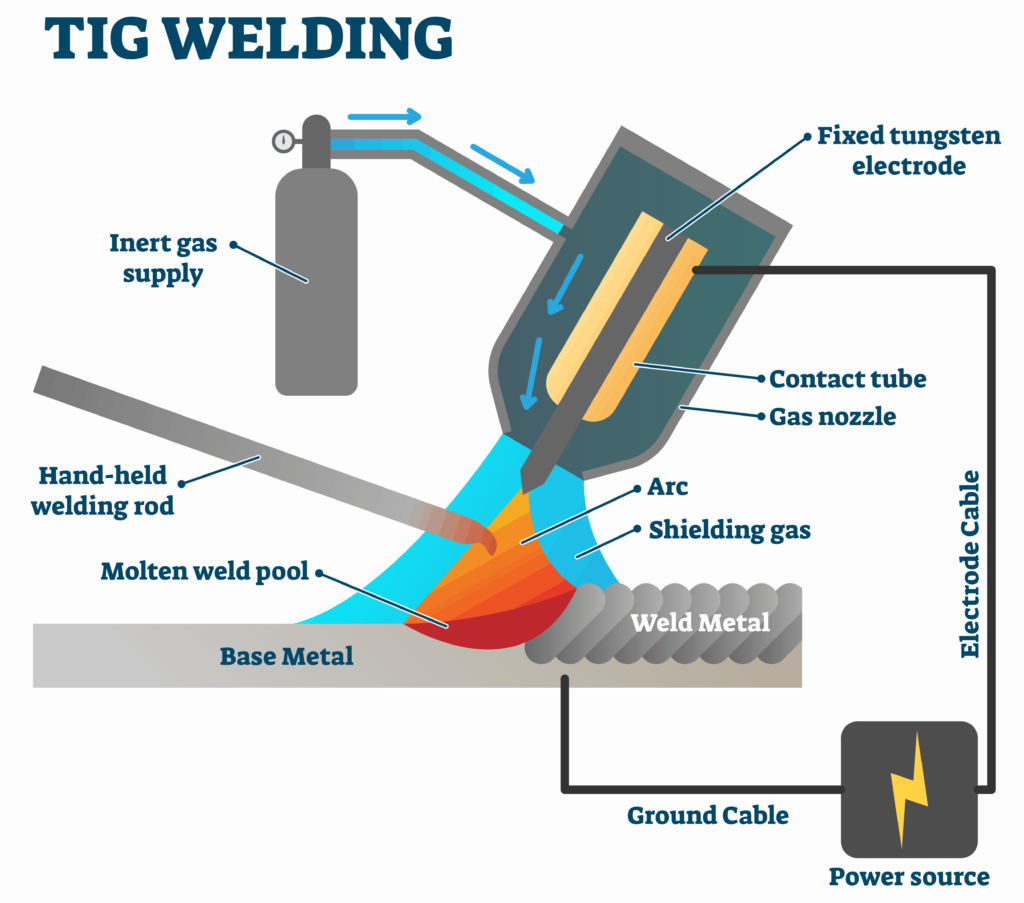
| Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, also known as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode and an inert gas, typically argon, to protect the weld zone. GTAW offers exceptional precision and control, making it suitable for critical applications, such as aerospace, automotive, and high-quality fabrication work.
|
|
|
|
4. Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
|
|
|
|
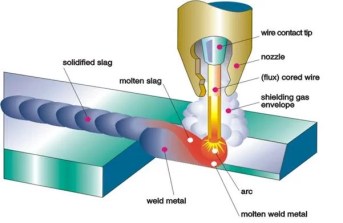
| Flux-Cored Arc Welding is a versatile method that uses a continuously fed tubular wire electrode with flux at its core. The flux produces a shielding gas that protects the weld from impurities. FCAW is preferred for its high deposition rates and ability to weld in various positions. It finds applications in construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing industries.
|
|
|
|
5. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
|
| Submerged Arc Welding involves the formation of an arc between a continuously fed electrode and the workpiece. The weld zone is protected by a granular flux that creates a blanket, shielding it from atmospheric contamination. SAW is highly efficient and used extensively in heavy fabrication, pressure vessel manufacturing, and large-scale welding operations
|
|
|
|
6. Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
|
| Laser Beam Welding utilizes a concentrated, high-energy laser beam to melt and join metals. LBW offers exceptional precision and is used for intricate welds in industries such as electronics, aerospace, and medical devices. It allows for minimal heat-affected zones and can weld thin materials with minimal distortion
|
|
|
|
7. Resistance Spot Welding (RSW)
|
| Resistance Spot Welding is a method that uses the heat generated by the resistance to electric current flow to join metals. RSW is widely used in the automotive industry for joining sheet metal components, such as body panels and frames.
|
|
|
|
| Welding methods play a crucial role in the fabrication and construction industries, enabling the creation of strong and durable metal structures. Understanding the different types of welding methods and their applications is essential for selecting the most appropriate technique for specific projects. Whether it's SMAW, GMAW, GTAW, or any other method, each has its unique advantages and considerations. By harnessing the power of these various welding methods, professionals can deliver high-quality welds that meet the demands of diverse industries.
|
|